- Leading Cable and Wire Manufacturer-ZW
- Control Cable
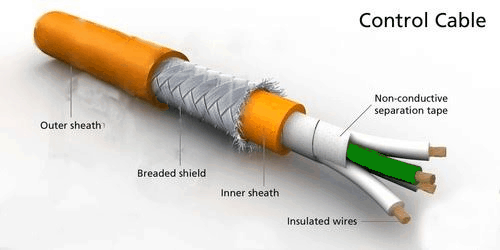
Control Cable
- According to IEC and GB Standard
- PVC Insulation and PVC Sheath
- Approved by CE, CCC, BV, SGS
- Large stock control cables with different sizes
The Astounding Features And Types Of Control Cable
Control cables are essential in electrical power generation and control. Without them, it would be impossible to get electrical energy to your homes and power your appliances. It would also be challenging to use electrical machines in manufacturing industries that use automation and instrumentation.
Different types of cables exist, but the ones relevant to manufacturing processes, communication, automation, and instrumentation are known as braid shielded control cables. These cables have specific applications in airports, ships, commercial centers, clinics, etc.
The different control cable types that exist include CY and SY cables. Most electrical control cables are usually buried in a building during installation. What set most control wires aside are their automation and instrumentation applications.
1. What is a control cable?
Control Cable, also known as flexible control wires or kvv cable, are multi-core cables designed for a wide range of automation and instrumentation, such as signal control, signal measurement, signal transmission, and signal regulation. These controlcables can be foil shielded, braid shielded, or both.

Leading Cable and Wire Manufacturer-ZW Page Shielded Cable According to IEC and GB PVC Approved
Cables are also often referred to by their type, size, and other specifications. This includes armored control cable, PVC control cable, SY flex cable, 6mm SY cable, 4mm SY cable, shielded control cable, power control cables, and push pull cable.
Control wires are often produced with tinned copper braiding to avoid electrical interference or the spreading of occurring electromagnetic fields. They come with an outer protective sheet, which makes them applicable for use under harsh environmental conditions. Depending on their construction properties and application areas, users often use flexible cables under light, medium, or high mechanical stress conditions. Control wires in industries are needed to supply current to the electric motor. They commonly have a green/yellow earth conductor in the outer layer of the twisted assembly.
Control wires are often referred to by specific applications such as robotics cable, instrument cable, industrial control cable, flexible control cable, auto control cable, automotive control cable, lszh control cables, etc.
The most important factors to consider while selecting a wire control are flexibility and the purpose intended for the cable. Different cable construction is required to use a flexible control wire in process automation and needs to be flexible enough for ergonomics in instrumentation applications.
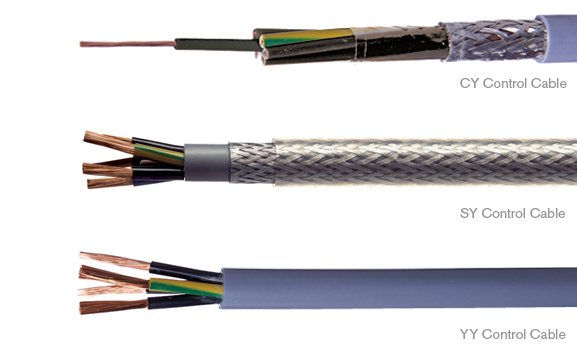
The most common control cables type is CY cable, SY cable, YY cable, LiYCY, and LiYY cables.
Each of these cables has unique degrees of protection against electrical interference, caustic resistance, and resistance to oil. CY cables are essential for areas where transmission must be free of electromagnetic interference. SY cables are flexible cables with additional mechanical protection, making them suitable for harsh environments.
YY cables are applicable in environments with light mechanical stress.
It is best to use LiYCY and shielded cable where moderate mechanical stress and electromagnetic screening is required. And lastly, LiYY cables are unscreened and unshielded light duty cables used in dry and humid environments.
Other types of control wires are LiHH cable and LiHCH cable.
2. What is a control cable used for?
Control cables are quite important and have a wide range of applications in assembly lines, robotics, and power distribution. They are often used to measure and regulate transmissions of automated processes.
The control wires are mainly designed for the command control circuit, centralized control of electrical equipment, and automated processes. For these reasons, control wires are fit for mining and industrial enterprises. They are used as protection lines and for the exchange of rated voltages. They also have applications in energy transportation.
3. What is the difference between CY and SY cable?
CY and SY cables are different in their construction and look. However, both CY and SY have a voltage rating of 300/500V.
The following are notable differences between them:
- The major difference between the CY control cable and SY cable control is that the CY control wire is better suited for interference-free transmission. In contrast, SY cables are used when your cable specification requires more reliable mechanical protection.
- CY is a multiple-conductor cable braided with tinned copper wire and an inner sheath.
- The sheath in CY cables is commonly grey, while a transparent jacket covers the SY shielded cable.
- SY Cables offer little protection against electrical interference but increase the mechanical protection of the cable. The reverse is the case for CY cables.
- CY cable control is a shielded flexible cable, while SY is an unshielded control cables.
4. Control cable vs. Power cable
Both power cable and control wire are common cable types. However, both are not the same.
The following points highlight the differences between power control wire and electrical cable:
- Control wires are electrical equipment cables, while power cables are electrical energy transmission and distribution cables.
- Control wires are annealed conductors, while copper and aluminum cover power cables. Most electrical conductors are made up of either of these two elements since they are good at controlling heat and do not melt away at a higher voltage.
- Control wires are best for controlling electrical hazards in many places. Places, where they are used, include building, construction, and the railway industry. Power cables, on the other hand, can most likely be found in electrical energy transmission and distribution sites and industries with heavy machines.
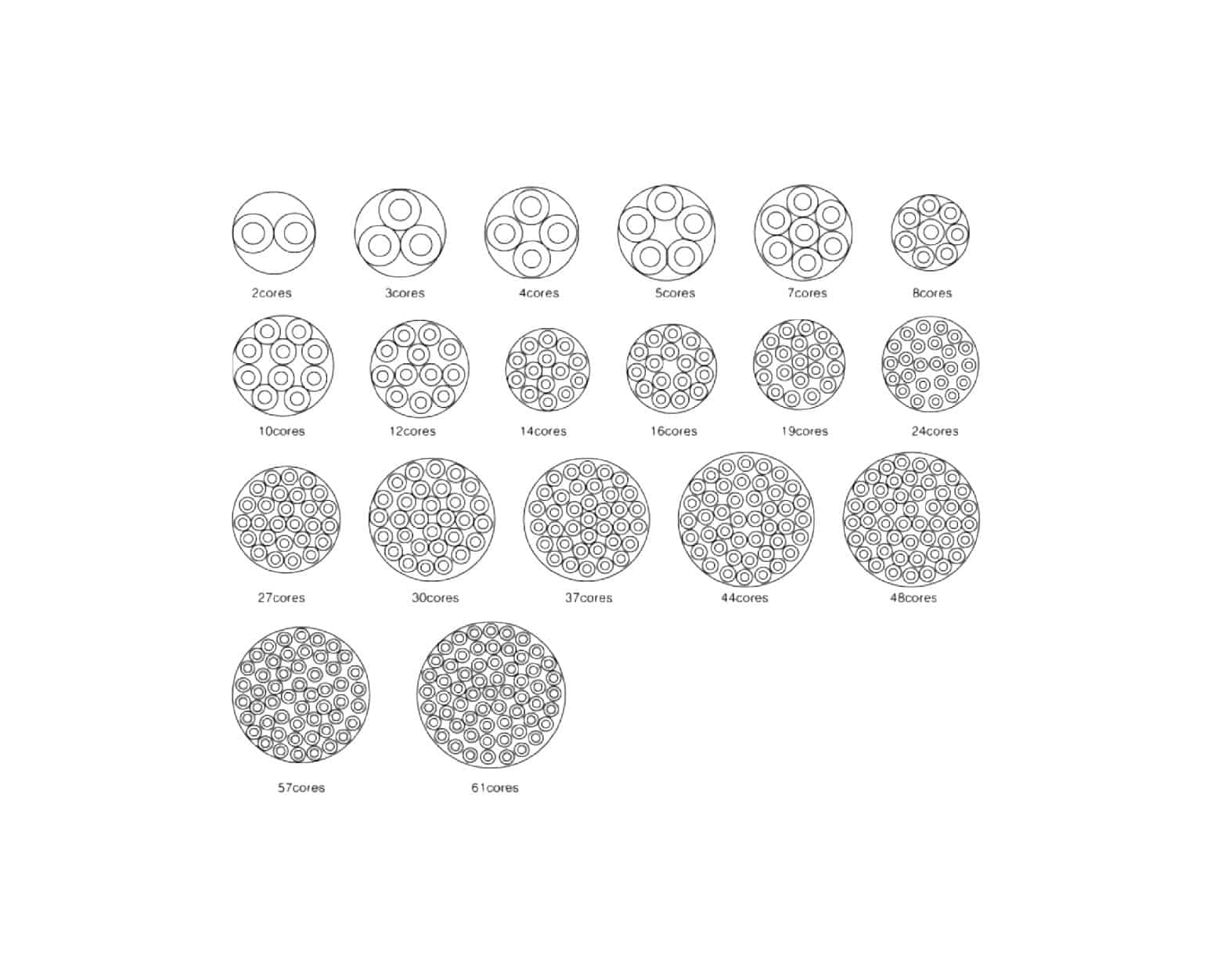
- Power cables are made for transmitting electricity, while the custom control cables act as controlling agents in the various process automation fields (the range of the kvvr cables goes up to 61 cores).
- Electrical Cables transmit and distribute high-power electrical energy in trunk lines of power systems and are usually buried in the ground during installation, not confined to a building. Simultaneously, control low-power (compared to power cables) electrical energy to machines and equipment. They can either be buried underground or within an organization when installed.
Also See:Underground Cable: Expert Answers To 5 Critical Questions
- Electrical cable operates at various voltage levels of 1-500KV and is above 0.6/1KV. Meanwhile, Cable control is mainly 450/750V, within 0.6/1kv.
- Low voltage cables in terms of size are larger than motor control cables.
- Power cables have a thick outer sheath compared to control try cables.
- Power cables often have a unique color code system that distinguishes the high voltage carriers from their low voltage counterparts. At the same time, the control wire cable doesn’t have color-coding.
- Control wire offers superior resistance to electromagnetic interference, which makes them ideal for sending low voltage signals. Power cables, on the other hand, are equipped to transfer energy to that equipment.
- Power cables can transfer both high and low energy from the source to the equipment, while power and signal control cable can only transfer low energy to the equipment.
- The power cable products always has a thicker sheath, while the control wire has a thinner sheath.
- Power cable operates the standard :IEC 60502-1,GB12706, while control voltage cable operates the standard :GB/T9330-2008,BS5308-1:19,BS5308-2:1986
5. Control Wire vs. instrument cable
Control wires send signals to control the functioning of a machine or equipment. They belong to the family of instrumentation cables, i.e., cables and controls that allow the distribution of data or signals with low voltage. This is to say that the difference between control and instrumentation cable is mainly in their usage. Either of them can be solid core wire or stranded wire. Control and instrumentation cables are designed especially for automation controls.
Instrumentation cables are best suited for regions that require less than one ampere. They can carry signals up to 40 volts. Like control wires, instrumentation cables are multiple conductor cables. They have applications in broadcasting, mass transit equipment, and industrial equipment control. They are also ideal for pressure meters, encoders, flow meters, programmable limit switches, load cell monitors, programmable controllers, and so on.
The notable differences between control wire and power cable are:
- Control wires do not require shielding, while instrumentation cable requires shielding.
- Instrumentation cables are usually made of stranded wires and are more flexible than control wires.
- Control wires have a larger diameter than instrumentation cables.
6. Bottom line
Control wires have various applications in manufacturing automation, aviation, instrumentation, etc. They are usually categorized based on size, specification, and application. Before purchasing any type of control wire, make sure to have decided on the type of flexibility you want and the area in which you intend to use the cable.
If you are unsure of control cable specification, simply read up on the common types of control wire that we have, i.e., Extensive research will help you figure out the best cable products for your needs. Don’t hesitate to visit ZW, your trusted control cable manufacturer. We will offer your high quality control cables.