- Leading Cable and Wire Manufacturer-ZW
- Instrumentation Cable
Instrumentation Cable
- According to IEC, BS
- Flame Retardant & LSZH, PVC Cable
- Approved by ISO, GB, SGS, CCC
- Large cables with different sizes
Instrumentation Cable: 5 Essential Facts to Guide You in Your Selection Process
An instrumentation cable plays a critical role in various manufacturing and processing projects. It is not easy to observe and control electricity systems and their supplementary processes without this cable. It transmits low-energy signals that you can use to regulate or keep an eye on various crucial functions that rely on electronic circuits.
State-of-the-art wireless transmission mediums have simplified signal broadcasts. People are accustomed to transmitting and receiving information wirelessly. Most of us lack meaningful knowledge on shielded instrument cable because we live in a world where wireless transmissions are trending. This cable transmits signals in electric circuits and is pertinent across various industries, including;
- The petrochemical industry
- Fertilizer plants
- Cement production plants
- Steel industries.
This post provides some meaningful information you ought to know, including types of instrumentation cables. Are you keen to find the best signal-transmitting wire that offers protection against interruption and interference? This is the best place to be.
1. What is an instrumentation cable?
An instrumentation cable is a cable that consists of several conductors whose purpose is to convey low-energy electric signals. Cables and electrical wires take up a plethora of responsibilities in various industrial applications. For example, they transmit electrical power, signals, or data. Generally, a cable is structured depending on its intended application and is equipped with different forms of protective elements.
Instrumentation cable manufacturers build these cable types to offer adequate shielding against any form of external signal interference. Their core function is to monitor and regulate various electric systems and their associated processes. Essentially, they assist in facilitating the smooth functioning of different industrial processes. It is also crucial to note that these cable types are typically applicable in microprocessor grounded and computer-based instrumented systems.
These cables come in handy in many control and communication applications because they are immune to external interruptions and interferences. They come in handy in process regulation, relay of analog or digital signals, voice transmissions, signal relays, and control circuitry. It would be best to settle for a flexible instrumentation cable due to the nature of its applications. This is the best cable to go for if you desire a signal transmission cable for the process, petrochemical, fertilizer and steel industries.
2. What are the types of instrumentation cables?
Typically, instrumentation cables are applicable in a wide array of industries. They are suited for harsh environments and have outstanding electrical, thermal, and corporeal features. However, they come in different assortments depending on insulation material and mode of shielding. Here is a comprehensive outline of different instrumentation cable types;
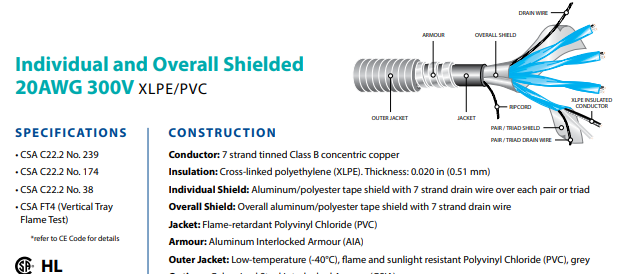
(1)PVC instrument cable (individual and overall shielded variants)
As the name suggests, this cable variation comprises a Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) outer coating. PVC is arguably the most popular thermoplastic insulation material owing to its impeccable features. The material is characteristically resistant to fire, any form of scrape, and moisture. The cable’s conductor material is copper, which is known for its top-notch electrical conductivity. More importantly, it meets several essential cable construction standards, including BS-EN-50288, UL 2250, EIL 6-52-46, etcetera.
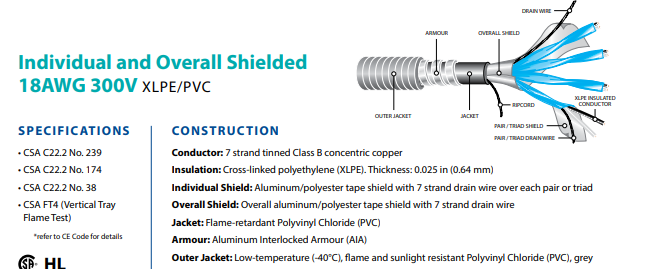
(2).XLPE instrument cable (individual and overall shielded variants)
The XLPE instrumentation cable is constructed with top-of-the-line thermal and moisture resistant cross-linked polyethene material. This type of insulation material features strong molecular three-dimensional bond structures. The wire can withstand any form of external adversity, including exposure to UV rays and oil. Like the PVC instrumentation cable, the cable’s construction consists of highly flexible stranded copper conductors for maximum electrical conductivity.
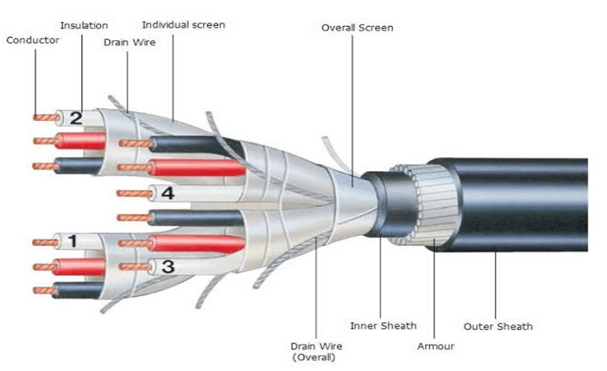
Regardless of the instrumentation cable types you opt for. You have to remember that there are different shielding methods. The shielding variations for this type of cable include;
(3). Overall Shielded Pairs/Triads
(4).Individual Shielded Pairs/Triads
3. What is the difference between instrumentation cable and control cable?
Most people, especially those that lack electrical cable expertise, confuse an instrumentation-type cable with a control cable. This confusion often arises because control wires belong to the instrumentation cable family. It is important to remember that there are some vital differences between these two cables when shopping for an ideal option.
The core difference between these cables rests in their usage. Control cables are typically helpful in situations that require larger wires that can withstand colossal electrical currents. Unlike KVV cables, instrumentation-type cables have a smaller diameter and have stranded conductors that guarantee maximum flexibility. Consequently, it is advisable to go for a flexible instrumentation cable if you intend to perform wiring applications that require maximum flexibility.
Also, instrumentation cables have shields to stop any electromagnetic interference that might impair their functionality. Generally, there are two types of shielding that cable manufacturers use: foil-type shielding and braid-type shielding. Unlike a control cable whose circuit does not require shielding, a shielded instrumentation cable is vital for all instrumentation applications.
4. Which instrumentation cable is ideal for the chemical and fertilizer industry
Apart from the instrumentation cable size, you ought to consider the cable type when selecting an ideal choice. Most people find it challenging to pick out the perfect option for the chemical and fertilizer industry. Typically, cables used in these industries face several hazards. There are two types of instrumentation cables, namely, PVC and XLPE. So, which is the ideal instrument cable option for the chemical and fertilizer industry?
It would be best to use a PVC instrument cable for such environments. Polyvinyl Chloride is a thermoplastic material generated through the polymerization process. This process produces insulation material resistant to flames, fires, repeated abrasions and moisture.
PVC is also known for being lightweight, resistant to corrosion, weathering and chemicals. Consequently, a PVC insulated cable is the ideal option for the Chemical and fertilizer industries. However, you need to check the instrumentation cable specification and ensure that it suits your specific application.
5. What are the key technical specifications of instrumentation cables?
Most people tend to confuse a standard instrument cable with an instrumentation one. This confusion often arises because these cables share many similarities. The images below portray different specifications of an instrumentation cable to help you distinguish them;