- Leading Cable and Wire Manufacturer-ZW
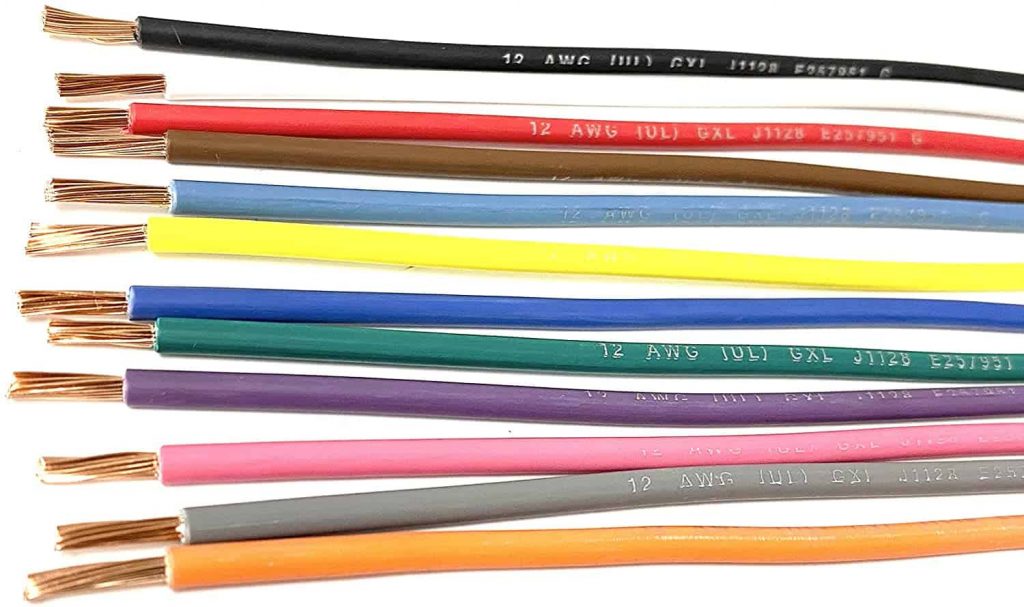
- 12 Gauge Wire
- According to IEC Standard
- PVC Insulation
- Approved by CCC, GB, UL
- Large stock
12 gauge electrical wire
Table of Contents
1. What Is 12 Gauge Wire?
The wire gauge is merely a measurement of the wire’s diameter or thickness, so a 12 gauge wire has a diameter of 2.05 mm and has lower resistance to current flow. They are utilized in the kitchenette, washroom, outdoor receptacles, including 120 volts air conditioning units that can handle up to 20 amps of power. This wire gauge has a diameter of about 2.05 mm. This kind of wire has to be produced following AWG standards. Typically, the thinner the wire, the greater number of the wire that can be put together. In cases where a large power supply is needed, a 12 gauge electrical wire is recommended for improved power transmission.

Leading Cable and Wire Manufacturer-ZW Electrical Wire According to IEC 60502-1, GB Class 6 Copper Conductor Approved by IEC, GB
Figure 1: 12 gauge flexible wire
It is also important to note that quality has little to do with the size (big gauge or small gauge) of a conductor’s wire gauge. However, a smaller gauge like a 12 gauge cable helps you get more conducting wires. Usually, the wire resistance should be less than 5 percent of the total standard resistance of 12 gauge stranded wire. With 1000 feet of 12 gauge copper wire it is possible to lose up to 1.588 ohms. It is possible to run this 12 gauge speaker wire with a 4-ohm speaker and 120 feet with an 8-ohm speaker.
Because 12 gauge aluminum wire is stiffer and 40% less conductive, it is advisable to use 12 gauge solid wire. With the massive front speakers, you can use 12 gauge wire electrical, while the remainder of my speakers is wired with 14-gauge. For this reason, purity and capacity to resist corrosion are highly solved.
There is always a concern about the usage of 12 vs 14 gauge wire, but should be known is that each wire gauge has its special use. It is easier for a larger wire to handle more current without overheating because it has a larger cross-sectional area. Larger gauge numbers correspond to smaller-diameter wires because the gauge is based on the number of wires that can fit through a standard aperture. So because 12-gauge copper wire typically measures 2.05 mm in diameter and 14-gauge copper wire measures 1.63 mm in diameter, the former is preferred in cases where overheating is prevented.
Figure 2: 12 gauge bare copper wire
2. How many amps can 12 gauge wire handle?
A 12 gauge wire rated for a maximum of 20 amps is typical. This amps capacity can be carried for about 400 feet on 12 gauge insulated copper wire. After that, voltage loss becomes an issue, and the gauge or voltage must be raised. Remember conducting electricity generates heat along the wire’s length. In other words, heat drains voltage, and the lengthier the wire, the more voltage you can lose.
Although the 12 gauge wire is rated at 20 amps, it is capable of carrying up to 25 amps. If you want to run wire to a workplace, it helps to be familiar with the 12 wire gauge size and the amps it can handle. It also comprises circuit breakers, so make sure you know whatever you do connect to and the exact amps you will need for your intended purpose. Otherwise, you run the risk of blowing the circuit breaker regularly and maybe sparking a fire.
Additionally, 12 gauge house wire can handle more than 20 amps under special conditions that are dependent on the conductor’s temperature rating. Amp allowances for 12 gauge aluminum wire and 12 gauge copper wire are governed by temperature ratings.
You may be interested in House Wire: The Safety Of Your House Depends On It
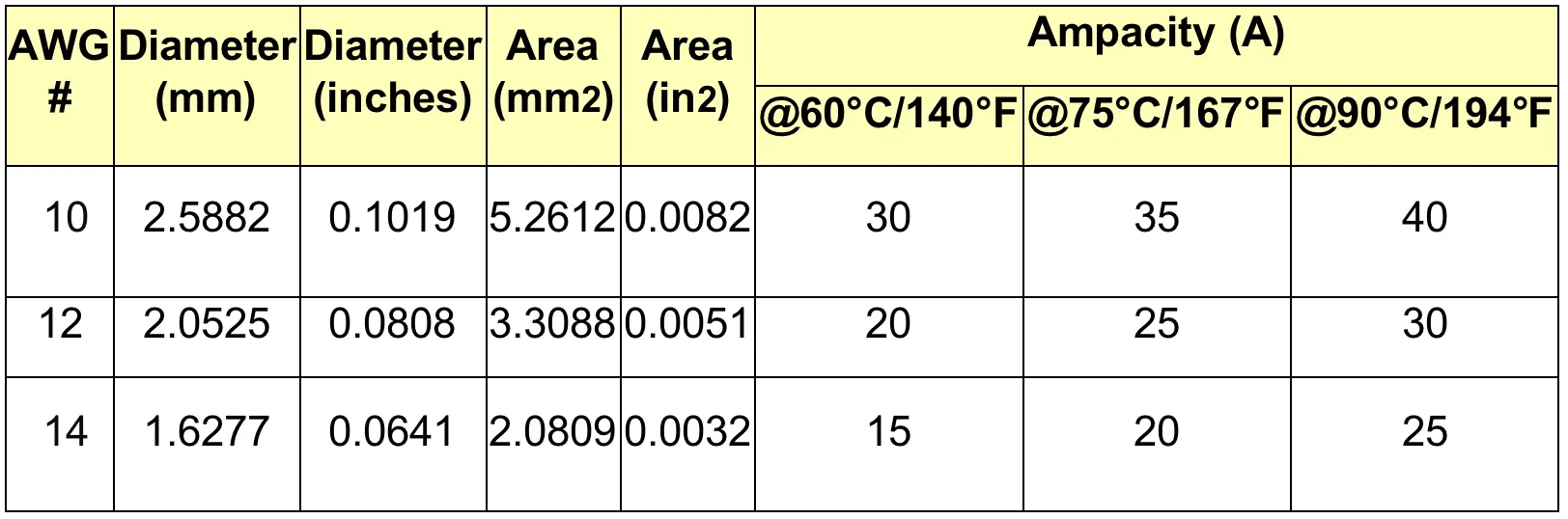
For 12 gauge copper wire conductors, at various temperature ranges like 60°C, 20 amps are manageable, at 75°C, 25 amps are required and at a temperature of 90°C, 30 amps are required. For a given wire thickness, the greater the heat rating, the more permitted amps are available. In most kitchens, 12 gauges copper wiring is used thus 12 gauge wire size matters in adjusting the number of amps that can be handled.
For 12 gauge aluminum wire, adjustments are as follows; at a temperature of 60°C, the output is 20 amps, and also at 75°C, 20 amps can be handled. An output of 25 amps is possible at 90°C. The reason for relatively lower figures in this scenario is that aluminum conducts electricity less well than copper.
3. How thick is 12 gauge wire?
A 12-gauge wire is typically 2.05 mm thick in terms of its diameter. The wire gauge relates to the wire’s thickness. Typically, the thinner the gauge wire, the greater its resistance. As a result of the increased resistance, the current flow will be decreased and the output voltage across the wire will rise. The metal ions clash with the traveling electrons during electrical conductivity.
This produces resistance and makes it very hard for the electricity to flow. A thin wire’s resistance is higher than a thick wire’s resistance since a thin wire has a lower density of electrons to carry the current. The 12 gauge thin wire, with a conductor diameter of 2.05mm, has the lowest resistance of the two gauge wires (22 and 12), which means that it has enough thickness that helps in safely conducting electricity.
Compared with a 14 awg wire, the resistance of a 12 gauge thin wire is lower than that of a 14-gauge wire because it is broader. The lower resistance of, 12 gauge high-temperature wire allows more charge to travel through it at a faster pace, allowing a bigger current to flow through it. As a result, 12 gauge wire is utilized in circuits with 20-amp plugs and circuit breakers. The 12 gauge wire amps are rated as 1.588 per 1000 ft or 5.21 per 1000 m. Other than a cross-sectional area which is a function of 12 AWG wire thickness, the resistance of the wire is also affected by length, where the longer the length the greater the resistance.
4. Is it 12 gauge wire vs 14?
A 12 gauge low voltage wire has a diameter of roughly 0.0808 inches (2.053 mm), whereas 14 AWG wire has a diameter of around 0.0641 inches (1.628 mm). It is thus 26 percent thicker and 59 percent larger in a cross-sectional area compared to 14 gauge wire.
A 12 gauge wire is required for an outlet circuit that is regulated by a 20-amp breaker while in a case where an overloading light circuit is not required a 15-amp breaker and wire 14 AWG are necessary. As long as the breaker and all of the outlets are rated for 15 amps and you can use a 12 gauge hook-up wire, to prevent both of these issues.
When a 20-amp breaker is installed, you have no option but to utilize awg 14 wire since the electrical regulations do not allow you to do so. Even though the appliances you put in are only rated for 15 amps, you must use a 12 gauge electric wire when plugging a 20-amp outlet.
Using a 12-gauge wire is a safe bet for wiring a circuit that includes both lights and outlets, or if you’re not sure which gauge to use. It is more expensive and less flexible than copper wire 14 gauge, but it is always a good idea to use it on a circuit rated for 15 or 20 amps. Using 12-gauge wire instead of 14-gauge is a good choice, even though the 12 AWG wire price is greater.
The highest current rating for a 14-gauge wire is 15 amps, whereas that for a 12 gauge automotive wire is 20 amps under typical residential settings. A 14-gauge wire may be used to connect a 15-amp light circuit to save cash and create the wiring work simpler. Two factors complicate the choice between 12- and 14-gauge wire for outlets: certain gadgets use more electricity when they first start up than their operating current, and circuits with numerous outlets might suffer severe voltage drops if a huge proportion of outlets are used simultaneously.
Other benefits of 12 gauge braided wire like 12 gauge 600-volt wire or 12 gauge thhn wire include usage in a wide range of applications, including residential, industrial, and commercial. For permanent structures, it is employed in the service entry and branch circuits.
5. What is the diameter of a 12 gauge wire?
The diameter of a 12 gauge wire is 2.05 millimeters. However, the diameter of a solid wire or 12 gauge bare copper wire and 12 gauge braided wire or a stranded wire is not the same. Solid wires have a smaller diameter than stranded wires. The 12 gauge bare copper wire also known as 12 gauge ground wire is the most often used grounding copper wire. Usually, the 12 gauge ground wire with a smaller diameter is used for ground wiring has no protective coating or covering.
On the other hand, 12 gauge insulated copper wire and 12 gauge braided wire with greater diameter provide some sort of insulation to safeguard the wire from electromagnetic fields to extend a wire’s flex life and boost its mechanical strength.
Additionally, 12 gauge marine wire is more substantial than 12 gauge automotive wire of the same size, despite both being coated. The 12 gauge marine wire has a higher percentage of copper than the 12 gauge automobile wire. Typically, the more copper in the wire, the greater the wire’s ability to transport current.