- Leading Cable and Wire Manufacturer-ZW
- Thhn Wire
- According to UL Standard
- PVC & Nylon
- Rated Voltage:450/750v
- Thhn wire temp rating-40 ℃~105℃
THHN/THWN-2 Copper Wire
Table of Contents
THHN Wire Buyers Guide: Getting the best value for money
Why is it important to know what THHN wire is, and what it can do for a project? When electrical engineers design the wiring specification for plant, machinery or buildings, they must understand what types of wiring are best for the job. Knowing the capabilities of THHN vs THWN cables and wires, and understanding which one to buy may often determine success or failure of the project. Why is that?
That’s because each projects’ wiring specs differ. For instance, THHN wire size of one application may not be suitable for another application. Similarly, your specifications might work better with THHN aluminum wire, but it might not perform optimally if you substitute it with THHN copper wire.
In this ZW Cable THHN Cable Buyers Guide, we’ll address some key factors about types of thhn, and discuss various points to consider when making procurement decisions. Remember, THHN wire price isn’t the only consideration for which wire to use. We’ll tell you what else you should factor into these decisions.

Leading Cable and Wire Manufacturer-ZW Electrical Wire According to IEC 60502-1, GB Class 6 Copper Conductor Approved by IEC, GB Temperature Range: -20°C to +70°C Nominal
1. What is thhn wire Meaning?
Electrical projects use various types of wiring. And within a project too, there might be different types of cables and wires necessary for various applications. THHN wire is a wire or cable produced per certain specifications. North American wire types must follow certain standards, including those defined by institutions such as Insulated Cable Engineers Association (ICEA), the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), and the national electrical code. One of those standards laid out is for thhn building wire.
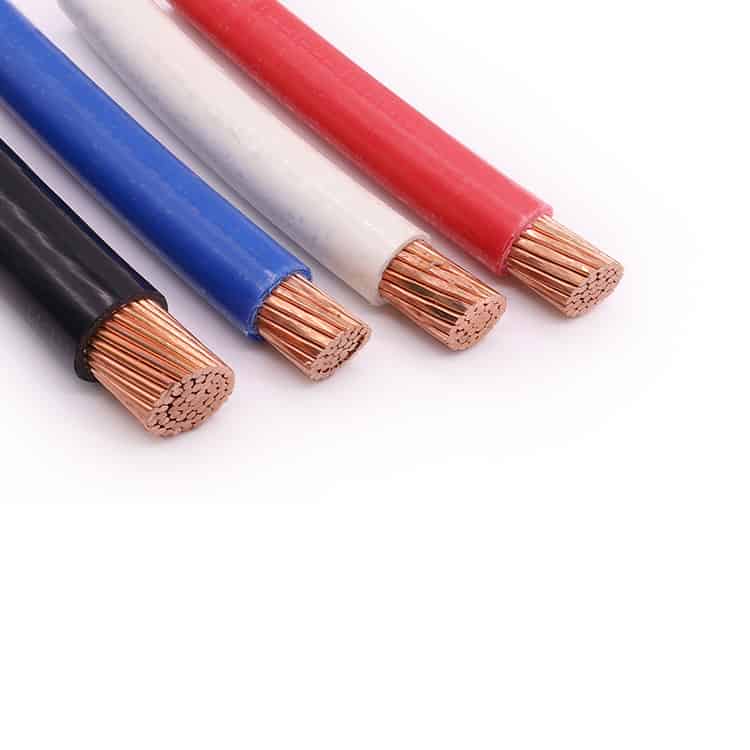
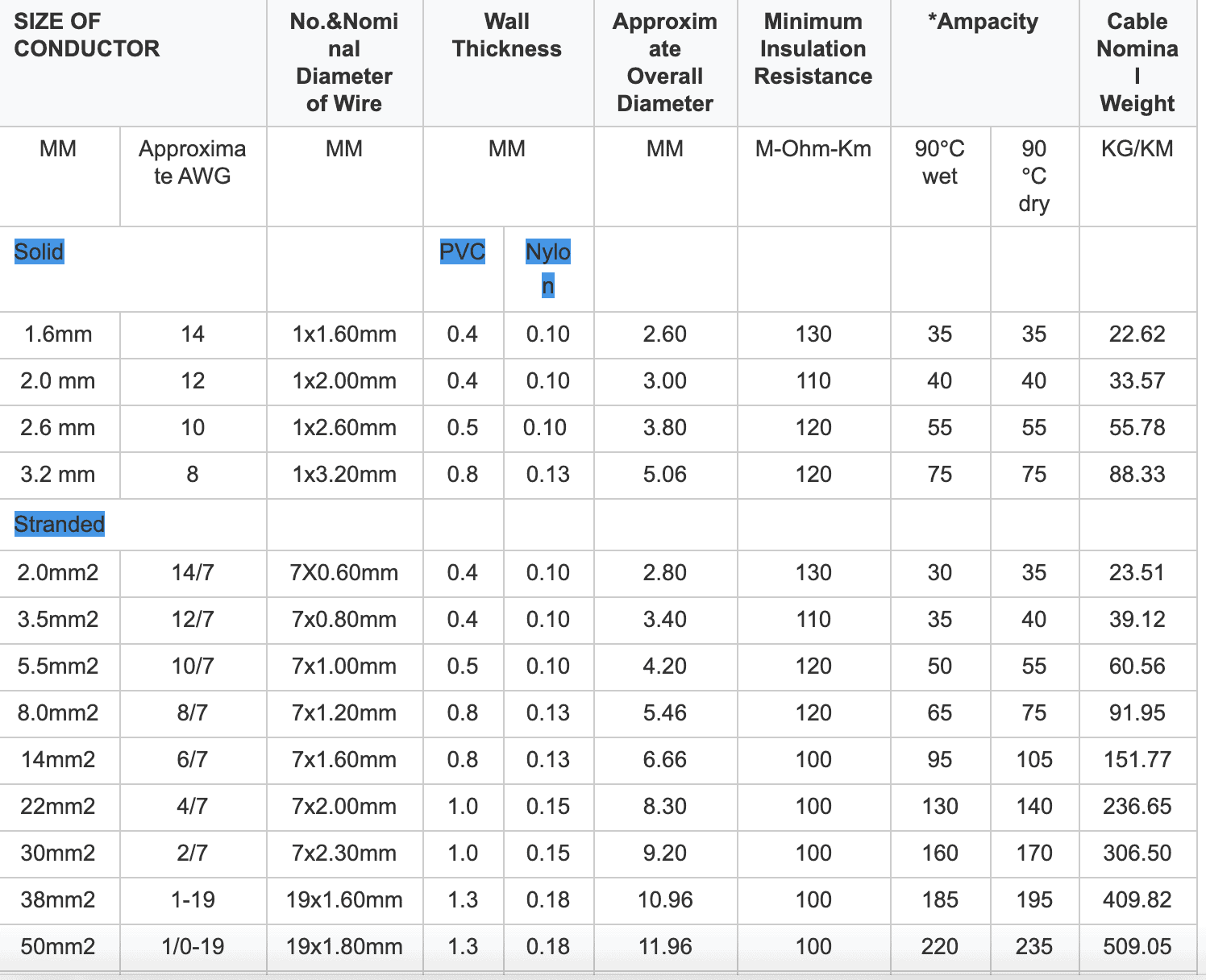
THHN is an acronym for “thermoplastic high heat nylon” THHN electrical wire defines specific temperature ratings, insulation materials, and conditions of use. Typically, these most popular type thhn wires are ideal for projects suitable for use in dry locations. Because of nylon jacketing, we also called nylon coated wire. Thhn wire stranded can be indoor and outdoor applications. Multiple thhn wires’ conductor are primarily used in conduit and cable tray.
THHN cables are popular type in building electrical transmission. Electrical projects may opt for either copper thhn wire, or they may choose THHN aluminum wire. Because of its high transmission rating – up to 600 volts – THHN cable is the ideal choice for industrial as well as residential and commercial projects.
2. What is the difference between AWG and Thhn wire?
Both AWG and THHN refer to certain manufacturing standards for producing hook-up wire. Manufacturers must certify their cables per these standards so engineers and project managers can choose the right product for their application. Both are acronyms defining those standards, and both thhn wire specifications to come from industry groups or certification bodies.

Leading Cable and Wire Manufacturer-ZW Page Hook Up wire According to UL Standard PVC, XLPE, Silicone Approved by UL, SGS, BV Different Colours Request A
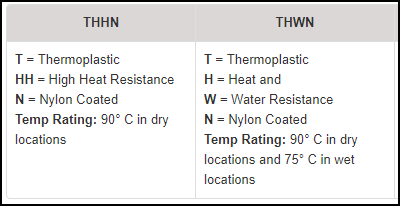
AWG stands for American Wire Gauge, and it governs the thickness of the wire. THHN cable, on the other hand, stands for “High heat resistant nylon coated”. It is a designation of the characteristics of the cable, including the rated temperature of the application, the insulation material of the cable, and what conditions the wire operates safely to deliver optimal value to the project.
AWG wire gauge governs the thickness (cross-sectional dimension) of the conducting copper or aluminum conductor used in the manufacture of XTHHN wire. It (the AWG rating) governs the amperage (or number of amps) that a type THHN cable may safely transmit. Generally, the higher the AWG rating (number), the less amps it can carry.
THHN wire size may also be measured in AWG scale such as 12thhn, #4 thhn, and #2 thhn but THHN primarily relates to the insulation of the cable. The purpose of insulation is to ensure current does not flow outside the confines of the insulation but travels within the THHN aluminum wire or copper conductor.
3. What’s the difference between thhn and thwn?
As noted earlier, different types of electrical cabling and wiring standards exist to guide engineers about which products are best for specific applications. When preparing to wire a building or appliance, it is important to understand which which cable’s ampacity to buy and use for the application. That’s where an understanding of THHN Vs THWN is vital.
A variety of electrical installations extensively use both type thhn thwn as well as THWN is essentially the same as thhn. THHN is a common choice when engineers want to connect branch circuits and for appliance wiring. THWN cable evolved from THHN cable, and like its counterpart is a nylon-coated but water-resistant wire. It (THWN) can function in similar operating environments as THHN, but without additional installation prerequisites to operate in wetter climates.
The major difference, therefore, between THHN Vs THWN, is the water-resistant feature of the latter over the former. Due to this additional characteristic (water-resistance), THWN has a clear advantage over type THHN cables: Due to its polyvinyl chloride coating coating, it doesn’t require additional conducting for safe installation. It may be laid out without a conduit, unlike THHN, which requires ducting.
As a result of this major difference between THHN Vs THWN, and because both types of cables have similar applications, many contractors simply carry THWN, instead of also hauling huge reels of THHN wire to job sites. Usually, if the contractor provides appropriate conducting for the application, it’s possible to substitute type THHN wire instead of using THWN cable. That’s because the specification for THWN allows it to function better in wet conditions where, unless you run it through a conduit, tffn and thhn cable might not be appropriate.
4. What is thhn wire used for?
Like it’s THWN wire counterpart, THHN wire comprises of a flame-retardant conductor and heat-resistant thermoplastic insulation. Manufacturers typically use extruded nylon – or similar materials – to produce the jacket. Depending on THHN wire diameter, it may be used for numerous applications, including control circuits, the wiring of machine tools, or in the electrical systems of various residential, commercial or industrial appliances.
THHN cable is often a critical component in North American AC electrical distribution systems, and are a good fit for voltage between 110 to 600 volts. Depending on the type of application and THHN wire size, project engineers may either use wires with stranded or solid conductors. Electrical project managers may choose to use either THHN aluminum wire or THHN copper wire.
Many wires may be dual-rated as 2THHN wire or THWN wire 12 gauge. These may work either for wet locations with temperatures up to 75°C (167°F), or in temperatures of up to 90°C (194°F) for dry applications.
5.What does thhn stand for?
THHN wire meaning stands for “Thermoplastic High Heat-resistant Nylon-coated.”. Type THHN wire is designated based on specific characteristics of the wire. These include temperature ratings, insulation materials used, and the permissible conditions for their use. Based on various criteria, including THHN wire size and the type of project, engineers may prefer THHN wire for both dry and wet conditions. Because of this dual usage (dry and wet)), most cable manufacturers label their THHN wire as THHN / THWN meaning they are good in either dry or wet conditions.
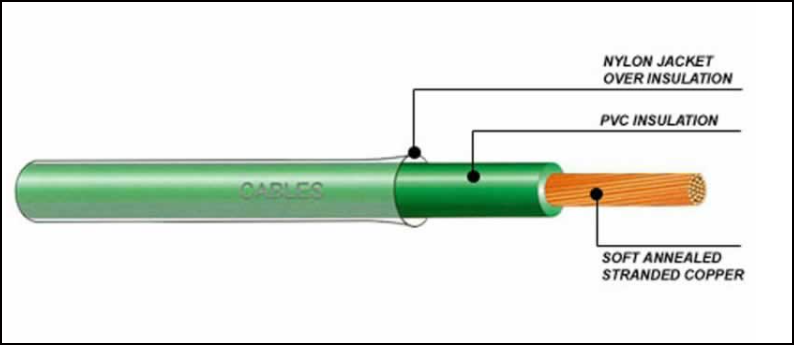
One characteristic of THHN cable is that its PVC insulation and a nylon jacket is comparatively (to other cables and wires0 is thinner, which influences the cables’ electrical properties. Under certain conditions, such as environmental exposure or contact with chemicals, current leakage may occur.Since the nylon sheath is a high-temperature material, it solves these problems perfectly.
The first letter, T, indicates that the insulation is a thermoplastic material made of tough heat and moisture resistant polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The middle letter (HH) indicates its high-heat resistance, suitable for use at temperatures up to 90 degrees Celsius(90ºc). The last letter, N, refers to the wire’s abrasion and heat-resistant nylon jacket. However, THHN wire price is often more competitive than other equivalent alternate wires, such as XHHW inexpensive building wire.
6. What features does a typical THWN and THHN cable have?
Depending on which type THHN wire you order, the cable may look slightly different. Typical choices include THHN aluminum wire or THHN copper wire. These come in either solid or stranded versions.
THHN wire size is determined according to the American Wire Gauge (AWG) size standards, which indicates the thickness of the conductor. Typically, THHN wire has three components to it. There is the inner core, which comes as either stranded or solid, depending on the THHN cable you choose. There is insulation that sheathes the core (conductor), and that insulation may be of PVC or similar material. Finally, most reputable THHN electrical wire manufacturers provide an outer jacket, often made from nylon.
The outer nylon jacket offers better handling capability to the THHN (or thhn thwn 2) product. It (nylon) does not provide any great resistance to the overall cable against friction or moisture resistance. However, because PVC is moisture resistant, it protects the THHN copper wire or aluminum core from water or other forms of dampness.
7. Finding the right THHN Cable Manufacturer
If you go online, you’ll probably find many sites that offer “amazing” THHN wire price. Don’t let that fool you! When looking for wiring for a critical project, it’s vital that you also remain focused on the success of the project. Yes, price is an important consideration. But, when making THHN electrical wire procurement decisions, never underestimate the importance of quality.
In this ZW Cable THHN cable knowledge, we’ve highlighted some of the critical qualities in wire and cable manufacturing. Before placing your order, make sure the wire you purchase meets the highest manufacturing specs. If you order cables from a manufacturer without proper credentials or someone who has no expertise in THHN cable manufacturing, they may offer you a great THHN wire price like 10 thhn price per foot, but poor quality could result in fire hazards to your project.