- Leading Cable and Wire Manufacturer-ZW
- Shielded Cable
Shielded Cable
- According to IEC and GB
- PVC
- Approved by UL, CCC, CE, BV, SGS
- Large stock shielded cables with different sizes
A shielded cable is a transmission line that uses a metal mesh braid to wrap the signal wire, and the braid is usually red copper or tinned copper. The shield layer of the shielded wire needs to be grounded, and interference signals can be directed to the earth by this additional layer. So we will use it in the security system
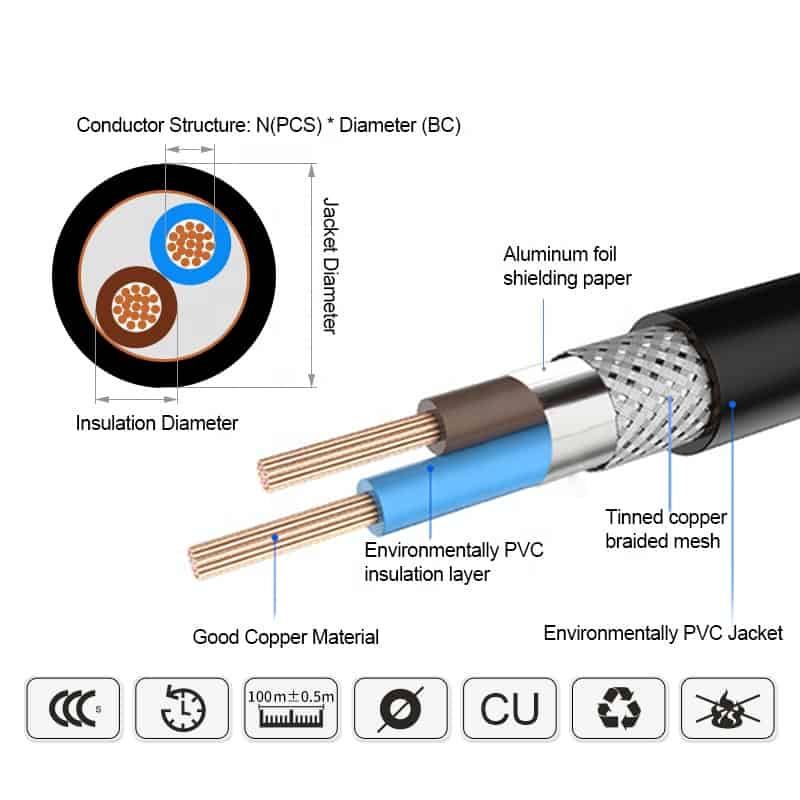
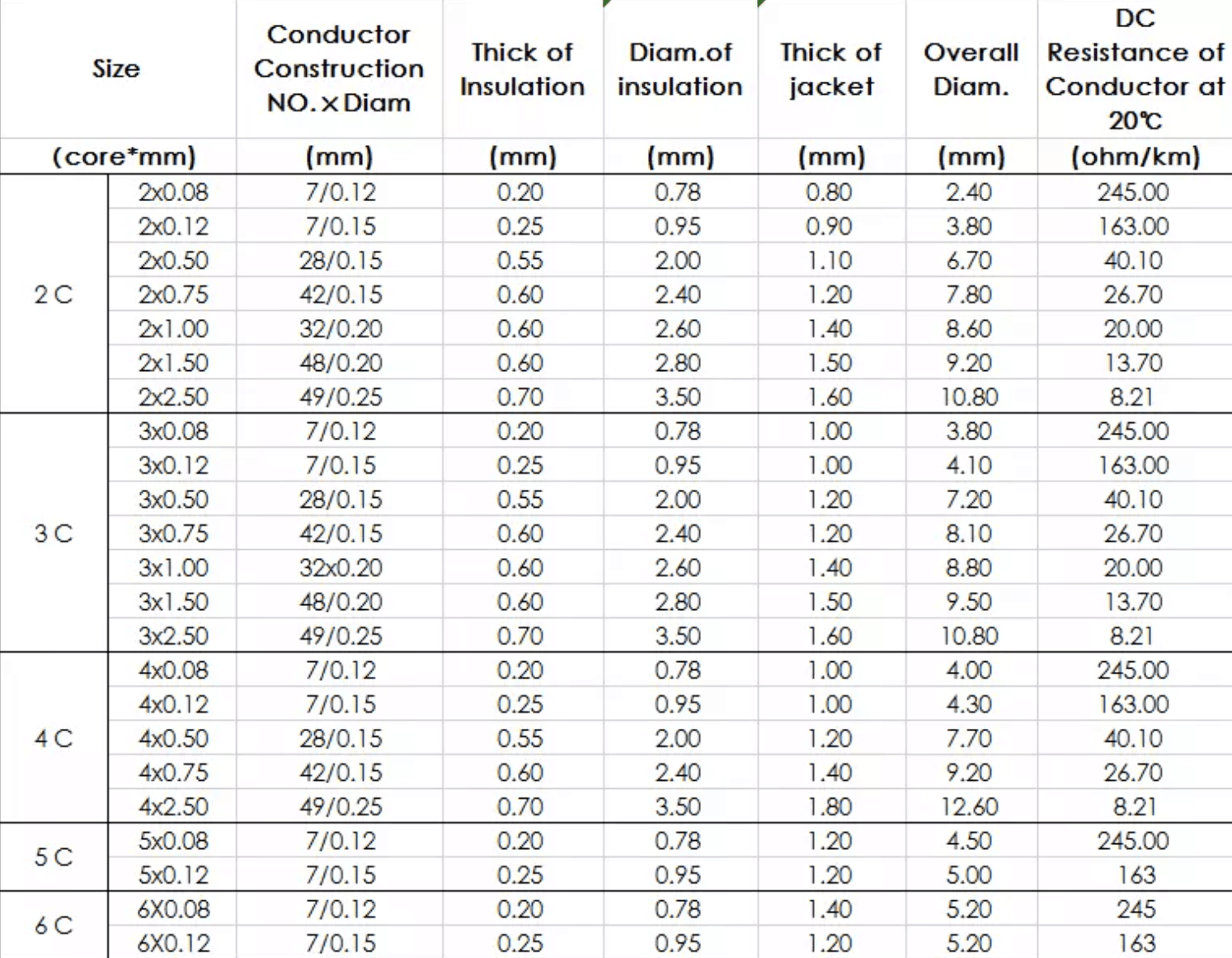
Conductor: Copper or Tinned Copper
Insulation: PVC
Shield layer: Tinned copper or Copper Wire
Sheath: PVC
Related Voltage: 300V/500V
Shielded cable types
Understanding Shielded Cable and Wire
Cables have played an integral part in transmitting various elements such as electricity and data over a long distance. This innovation has advanced over time and has seen several additions to its properties and features. With the introduction of several cables to serve their designed purpose, we have seen a rise in their acceptance. Each cable has the ability to carry out specific tasks, and most of these tasks protect users from harm that the subject of their transmission could cause.
A superb cable to note is the Shielded cable, which we will discuss in this post. Shielded cables are now a mainstay in the installation and fitting of many electrical devices and structures as their safety level is tested and trusted to deliver.
For this post, we would delve into the shielded wire’s workings and give our readers a better understanding of this subject.
What is a Shielded Cable?
Shielded cable is a specifically designed innovation used in an electrical installation that has insulating conductors encapsulated inside a standard conductive layer. These cables come in several builds and are designed to all follow the same principle as stated above. Shielded cable manufacturers design the shields from any spiral copper tapes, braided copper or similar metals, and any other polymer conducting object. This is to help increase the protective barrier that cable shielding provides.
The dexterity of shielded wires makes them an excellent choice in electrical installations, as they are much safer than their counterparts. Mostly, the shielded cables can be tougher to handle due to their rigidity and thickness. A primary reason why lots of electrical technicians prefer the shielded cable is its ability to function correctly in the case where the installation is prone to electromagnetic interference. However, most agree that the shielded cable wire’s intrinsic nature makes its handling more complicated and lengthy.
So when it comes to installation, which requires industrial-level performance, the shielded wire is usually the best choice for most technicians. This is mostly due to its high safety levels and increased protection for the intended installation.
Types of Shielding
Since we have mentioned and explained what a shielded wire is, we would also have to understand the types of shielding utilized in these cables. There are several methods of shielding a cable to provide increased efficiency. However, foil and braided shielding are the two most common ways manufacturers use in their shielded cable production.
Foil Shielding: For foil shielding, the technique involves attaching a thin aluminum foil to a conductor to aid its protection and durability. This method is very secure, especially when grounding the cables, as it gives access to a connector due to its thin nature. Foil shielding provides durability, and total protection to the conductor, and it is lightweight.
Braided shielding: This method involves the braiding of a thin mesh of copper wire, which provides resistance albeit low, thereby allowing easy termination. This method makes the cable heavy and more expensive and has a chance for more effectiveness. This shielding style’s weave method provides a 70-95% chance of reducing electromagnetic interference depending on how tight the manufacturers weave the braids during production.
Another reason why braided shielding is widely accepted is that the material used in its production, copper, has a high conductivity instead of aluminum, which makes it perfect for manufacturing foil shielded cables. Although this shielded cable price is costly, it is worth it as it provides excellent value for your money
Unlike foil thin sheets, braid shielding does not provide total coverage of the conductor, and there are small gaps in the shield.
Why Use Shielded Cables?
You can quickly determine whether a shielded cable 4 core is the best for your installation by the level and classification of the installation required. Most times, people fail to understand the concept of shielded cables and what it offers users in the long run. However, understanding the need for shielded cable is essential, and having an idea about how this works would increase its acceptance.
For installations classified into the industrial level range, utilizing shielded cables is the best option. This is due to the high resistance these cables provide in protecting the content, which is usually transferred through it in the long run. Nowadays, since data is usually transmitted from station to station through cables and towers, we cannot overemphasize the need for shielded cables. As mentioned previously, the primary threat to data transfer is usually EMI or Electromagnetic Interference.
That is why the utilization of shielded cables is essential if you want to protect your data. This is why most facilities that utilize equipment that disperse electromagnetic waves ensure that they make installations using shielded cables, thereby increasing the protection of data from electromagnetic decomposition. Adding drain wire will ground a portion of the current, which will reduce the risk of safety.
When to use shielded cables
The choice of using shielded cables isn’t one prone to much debate, as the consideration of protection of data is more important than its transference. This is why shielded cable has become a generally accepted solution for combating the receiving and distribution of EMI. However, when is the best time to make use of shielded cables? Deciding on when to use shielded cables starts from the moment a decision is made that the infrastructure which needs the electrical installation would at any time transfer data. This is because any interruption from EMI could cause issues during data transmission.
The very fact that power cables, which play an essential role in the provision of electricity, are designed to be electromagnetic conductors. This choice is because they eradicate or reduce the prevalence of noise in that environment, thereby creating a barrier for the transference of data. The perfect solution to this is to have shielded cable manufacturers produce a method and way through which their twisted cables can bypass the noise and protect the data.
How to ground shielded cables?
In electrical installation practices, grounding is a crucial factor in providing protection and functionality of the system. The grounding process connects the electrical system to the ground and creates an avenue to eradicate electromagnetic interference and provide stability. This will help to protect your data during transmission
To adequately ground shielded cable wire, the shield should is grounded at the ends. This practice is widely accepted and the safest way to ground shielded cables; however, there is a possibility of the system experiencing ground loops. These loops are not dangerous to the electrical system but provide a loophole in this method. A popular method states that grounding shielded cables should only occur with the shield being grounded at one end, thereby eradicating the possibility of ground loops.
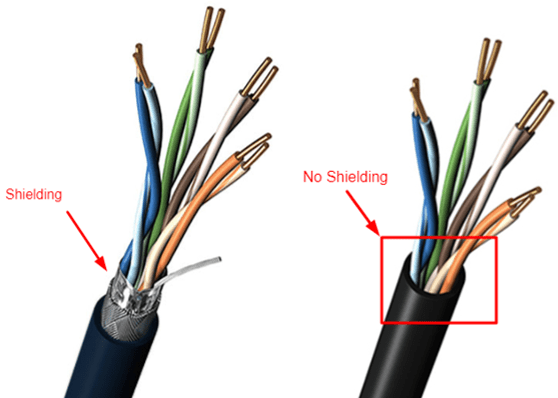
What is the Difference between Shielded and Unshielded Cables?
For several people, the choice between shielded and unshielded twisted cables is dependent on the several factors that bind both of these cables. As we have stated above, shielded cables have more possibilities of usage in certain quarters. However, both cables can possess functionalities that suit their various purposes. In order to shed better light on the advantages, and disadvantages of shielded twisted pair cables, let’s take a look at the features and properties of both cables. This will provide readers with the choice on which is best suited for their task.
Shielded Twisted Cables:
These cables are made with strength and capability in mind, as they are rigid and hard to handle. Shielded cables must be handled carefully and are suitable for installations that come in close contact with an environment prone to electromagnetic interference. Environments such as these include offices, radio, and television stations. This is because they counter and protect data from electromagnetic degradation, thereby keeping the data safe.
Shielded cables, also known as shielded twisted pair cables, are manufactured differently to serve various purposes. Manufacturers of shielded cables designed them to shield each pair of wiring or cable with a foil shielding for increased protection. These cables are shielded in several ways; however, below are two of the major cable types of shields used in the cable installation;
- Foil shielding
- Braided shielding
Unshielded Cables:
These cables are different from their shielded counterpart in their build and design, which are usually light. This cable’s light wiring system is protected by twisting each pair, inserting it into a tube, which would serve as its protection. This type of wiring or cable allows the reduction of electrical noise and crosstalk, which would bring about interference.
The unshielded cables are usually utilized in Ethernet cables and serve their function in the transfer and protection of data. The cables are usually cheap and also very easily accessible. However, they have a limited operation scope, as you cant use them in installation premises that utilize huge machinery and electronics.
In conclusion, deciding on which type of wiring to choose for your installation depends on several factors. However, installations that could bring about electromagnetic interference are addressed using shielded wire cables designed for that purpose. Once the price has been overlooked and the cables installed, the transference of data between locations can now be conducive, safe, and EMI-free.