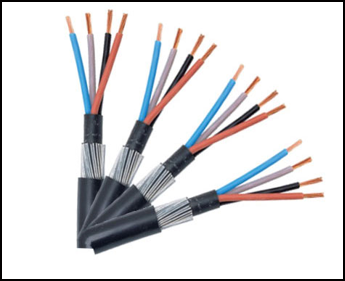
A 4 core cable is typically used in higher-level electrical applications. Where a typical household or residential project might use a single-core or 3-core product, like a 4mm wire, more heavy-duty projects – such as industrial and commercial uses – are better served by the use of 4mm 4 core cable. However, the choice of which 4-core product you choose, and how you wire the circuit may differ.
There are various types of four-core cables too. For example, a 4 core flex cable is a comparatively soft and pliable option for electricians to consider in some projects. Because of their relatively less rigidity, the 4 core flexible cable might be great in residential applications that require cables to pass through walls, under basements and over attics.
Then, there’s the hard, tough 4 core 2.5 mm armoured cable – a variety of four-core cables for heavy-duty, high-performance applications. The 4 core screened cable is the ideal choice for use in outdoor applications, or for projects where a lot of cabling passes through a densely cabled corridor. In these situations, the 4 core armoured cable protects the inner cores from exposure to the forces of external elements – heat, pressure etc. But it an armoured 4 core XLPE cable also helps protect the application from electrical and magnetic force interruptions.
1.What is 4 core cable?
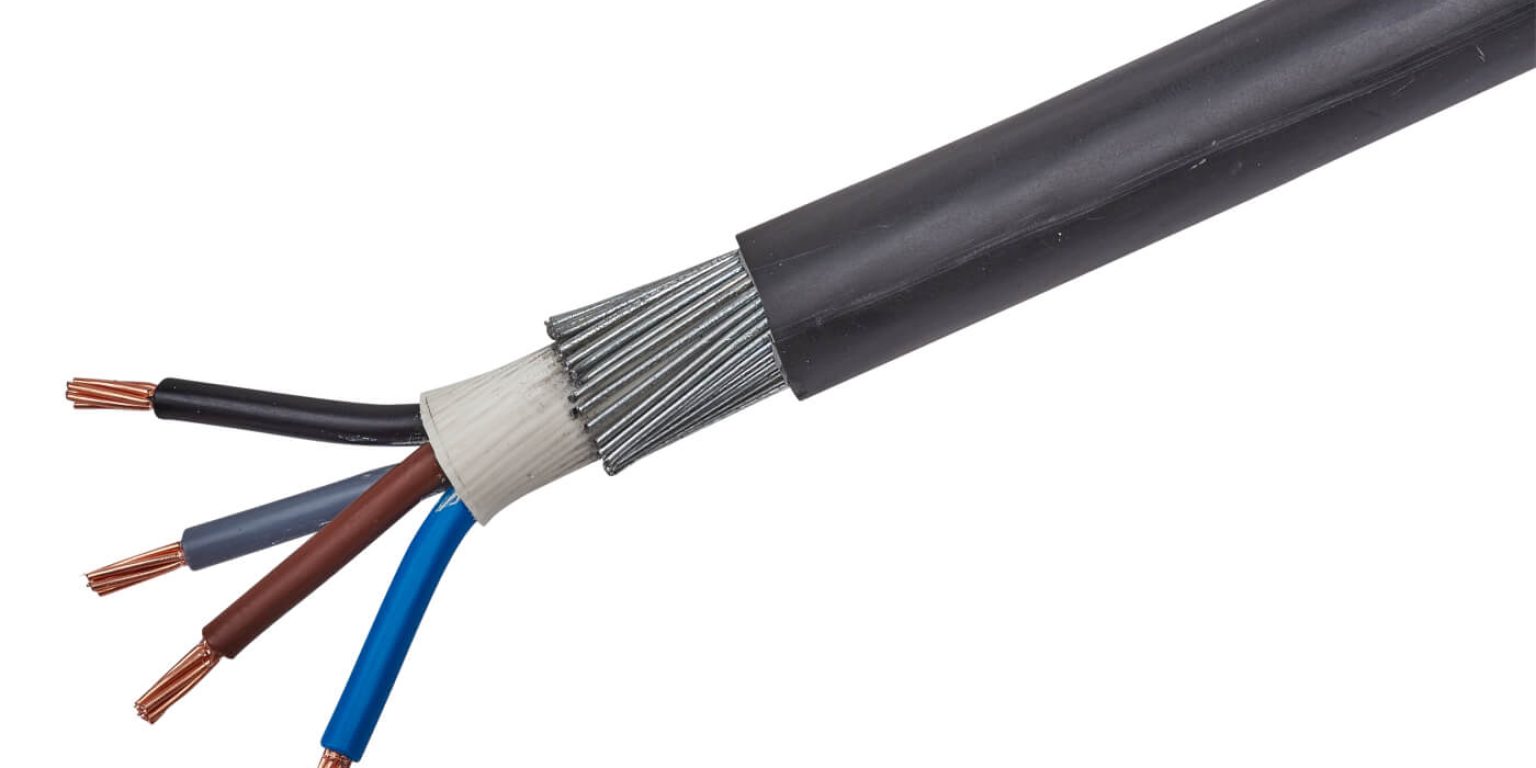
On the outside, a 4 core cable may look like a single, long piece of cable. When you look at the inside of the cable, however, you’ll see multiple conductors. Single core cables have one conductor, while multi-core cables have more than one. In the case of a 4-core cable, there are four separate conductors.
Typically, a good quality 4 core cable may come as 4 core electrical cable or these may also be available as 4 core armoured cable. A 4 core electric cable has the following specifications:
- Conductor: Copper
- Insulation is XLPE
- Sheath is PVC
4 core armoured cable usually has the following specifications:
- Conductor: Copper
- Insulation is XLPE
- Armoured can be steel wire tape and steel tape armoured
- Sheath is PVC
The size of all cores in a 4 core electrical cable remain the same. For example, in a 1.5mm 4 core flexible cable, all 4 conductors are 1.5mm in cross-sectional diameter. This is different from – for instance – a 3.5 core cable. If you wanted to buy a 16mm 3.5 core cable, the 3 phase conductors would be 16mm and one neutral conductor would be 8mm – i.e., half the size of the phase cables. However, for the same 16mm 4 core armoured cable, all four cores are 16mm.
2.What is 4 core cable used for?
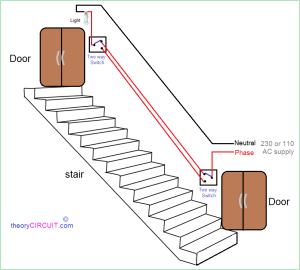
A 4 core cable may be used to create 4-wire circuits for electrical applications. For instance, one very common use of 4 core electric cable is in wiring two-way light switches using a 4-wire circuit, at the top and at the bottom of a staircase in a house.
An electrician might use 4 core 1 mm cable to wire two full electrical circuits. There’ll be one circuit in each direction that provide low cross-interference and deliver full-duplex lighting. Using a 4 core cable in this application allows people in the home to turn the light on and off from either switch, at the top of the stairs or at the bottom, independently.
Other 4 core cable uses might include external applications. For instance, a 4 core shielded cable is ideal to deliver power to external installations and equipment. If a homeowner wanted to deliver power from the main building to an outside shed, using a 4 core 1.5mm cable might be a great way to accomplish that objective.
3.What is 4 core Armoured cable used for?
Armoured or screened cable, such as a 4mm 4 core cable, are cables used in electrical applications where there’s a need for greater protection of the cable. You’ll see electricians commonly use them, such as 25mm armoured cable 4 core, in environments where the cable might sustain unusual amounts of stress or tension. The stress to the cable might arise at installation, when cables are tugged and pulled, or during operation when weights and tension bear on the cable.
A 4 core screened cable might also be used to protect cables from electrical magnetic interference (EMI) from other nearby sources of electricity. For example, if you used two sets of a 4 core 35mm armoured cable to power two sets of sensitive electrical equipment, there would be less electrical interference between the two (low cross talk). Unshielded cables might, on the other hand, compromise the integrity of the application.
Another great use of armoured 4 core copper cable is in underground applications. Typically, because those cables experience wet and harsher conditions than indoor cables, the cables need extra layers of protection. A 4 core shielded cable provides that additional protection is better than an unshielded version.
4.How to wire 4 core cable?
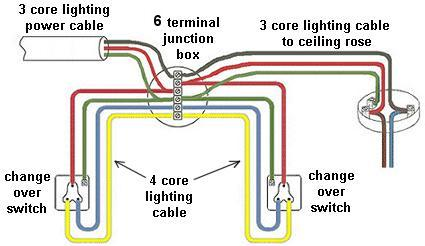
Typically, you wire 4-core cables for applications such as 2-way circuits. For example, you could wire this type of circuit to control an application running to the same location – a fan or set of lights controlled from two points.
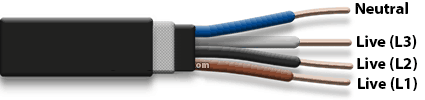
Whether you use 4 core flexible cable or single-strand hard cable, the wiring must conform to the applicable colour codes:
- Brown = L1 (Live)
- Black = L2 (Live)
- Grey = L3 (Live)
- Blue = Neutral
In most cases, when wiring 4 core electrical cable to residence, only a single phase is brought into the home from the mains distribution source.
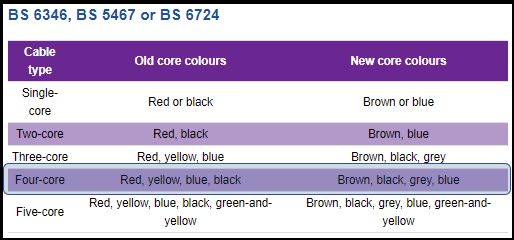
Under the revised British standard for electrical cables, 4 core cable colours have changed. The old colours for the four cores in a 4 core cable were Red, Yellow, Blue and Black. These are now replaced to Brown, Black, Grey and Blue. In the new regulations, Blue (not black!) is neutral. Brown is the hot (live) wire. This specification of 4 core cable colours must be kept in mind when wiring an application using four core wire.
5.What is 4 core electrical cable?
Normally, because of the heavy loads involved, 3-phase cables aren’t common in residential and housing applications. However, these are standard for other applications, such as high-rise rooming complexes, commercial and industrial applications, where the use of 4 core electric cable is essential.
For three-phased heavy-duty power applications, you may see cables such as 240mm 4 core cable used by electricians. The 4 core cable used here has four conductors, where each of the 4 core cable colours has a specific function. Three of which are live (L1, L2 and L3), with one acting as neutral. These colour-coded cores are individually covered in PVC insulation to keep them separate, grouped into a single 4-core cable and sheathed in an inner layer.
There are various types of 4 core electrical cable available. A common one is steel wire armoured cable (SWA), which is also called 4 core SWA cable. In this version, the cable has an additional layer of protection built into it. The inner sheath is covered in another layer – typically made from galvanised twisted steel wire. To complete the 4 core armoured cable, an outer layer of insulation is added which protects the SWA coating.
Another unique characteristic of 4 core copper cable is the insulation used when manufacturing the cable. You might see heavy-duty cables, such as 35mm 4 core armoured cable on the side on roadways and bridges. These have insulations made from material known as XLPE. The “XL” denotes Cross-linked – which identifies a technique of manufacturing the 4 core SWA cable. And then, the “PE” stands for Polyethylene – which is the material used in producing the insulation. Such cables are called 4 core XLPE cable.
Last Updated on June 27, 2022 by Richard