- Leading Cable and Wire Manufacturer-ZW
- Armoured Cable
Armoured Cable SWA & STA
- According to IEC and GB Standard
- XLPE & PVC Cable
- Approved by ISO,CE, SGS
- Large stock armored cable with different sizes
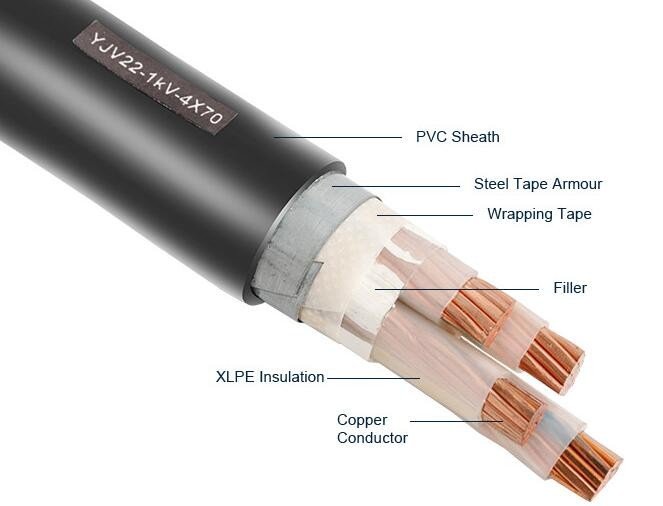
Armoured cable protective layer can be added to any structure of the cable to increase the mechanical strength of the cable and improve the erosion resistance. In addition, the purpose of adding armour layer to the cable is to enhance the tensile strength, compressive strength, etc., which can protect the cable and prolong its service life.
Table of Contents
With the development of the power industry and modern technology, the armoured cable is increasingly widely used for long-distance transmission projects of direct or alternate current. Armour cable is an electrical cable specifically designed for use in potentially hazardous areas.
The armouredcable can have better mechanical strength, which can resist external forces, so it is suitable to be laid in various complex environments. The armoured power cable mainly applied to railways, subways, high buildings, and other special occasions.
As the name suggests, armored cable has a protective layer, which can protect the inner wire of armour cable and ensure the safety of workers. Furthermore, armour cable is characterized by strong anti-corrosion performance because of the good material selection. Let’s dive in and learn more about the armour cable.
Construction of Armoured Cable
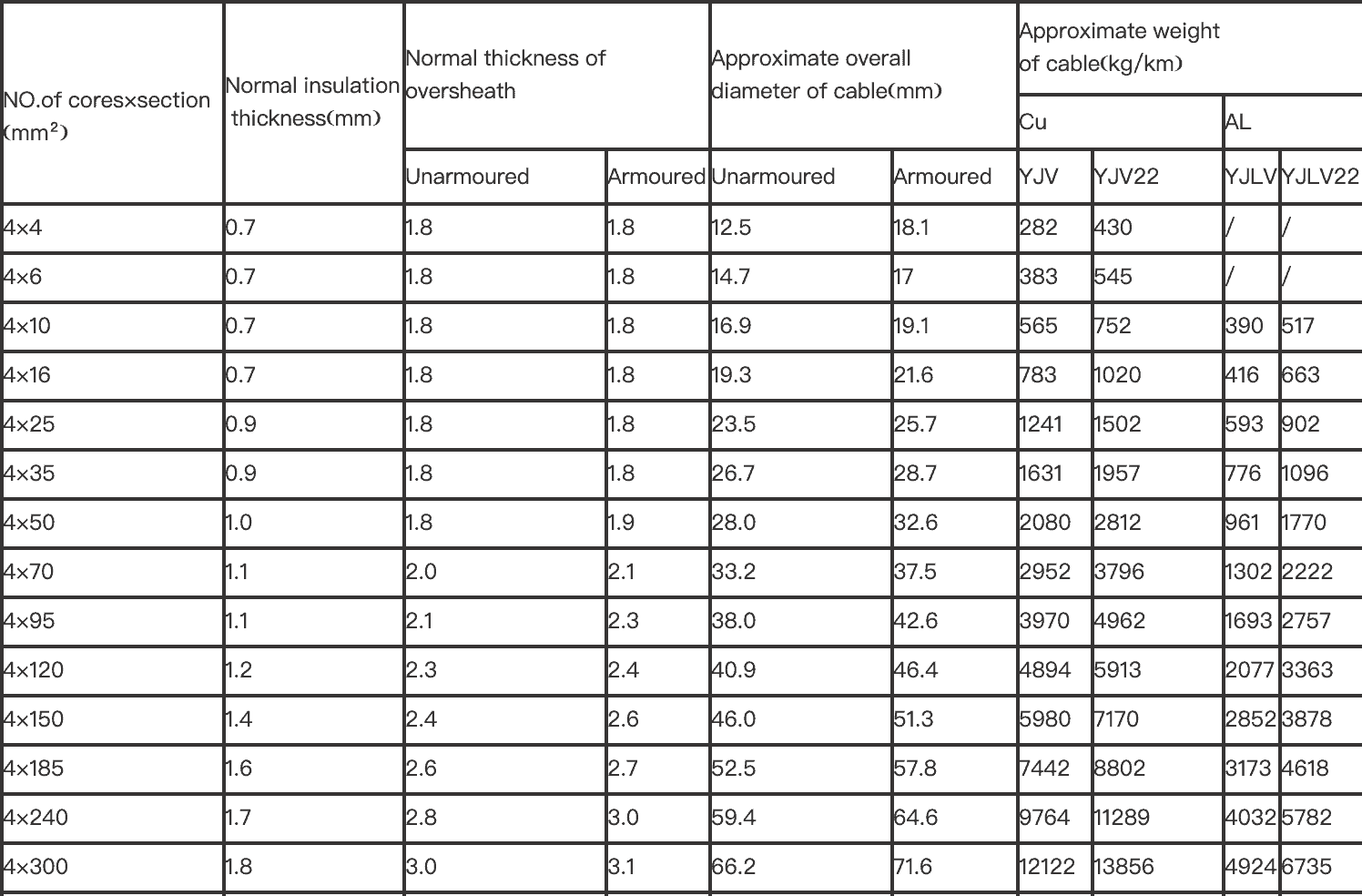
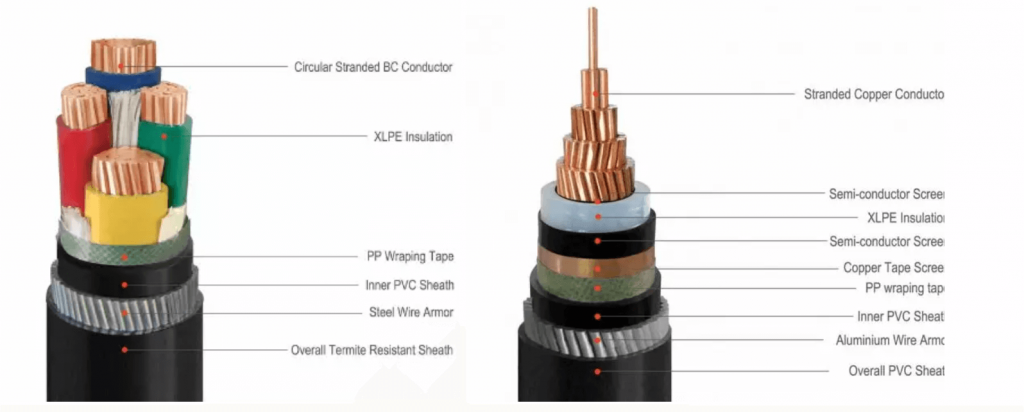
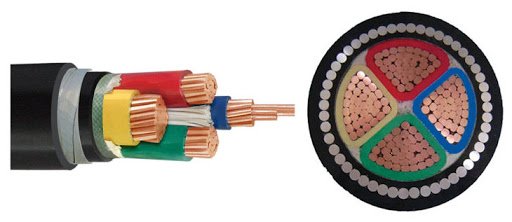
The construction is similar, whether it’s a SWA armored cable or PVC armoured wire. There are various armored cable cable types but most common type used today is steel wire armouring (SWA), a galvanized steel wire braid surrounding the inner sheath of the cable.
Armored cable construction is not much different from other types of power cable. But, adding the armoured layer or layers makes it suitable for more hazardous applications.
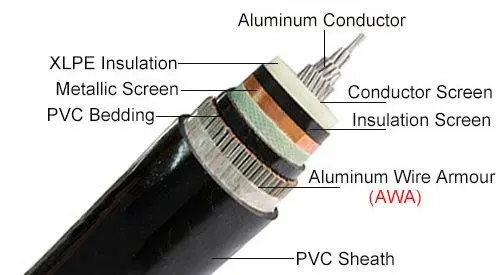
The armoured cable is manufactured with a range of cores such as 2 core armoured cable, 3 core armoured cable, 4 core armoured cable, and even up to 36 cores. Different armored electrical cables, including aluminum armoured cable and copper armouredcable, consist of the following components in their construction.
● Conductor
The conductor of the armour cable is usually made from stranded copper or aluminium. The armoured wire size (cross-section) of the conductor can be varied to suit the application, but the most common sizes are 16mm armoured cable, 25mm armored cable, and 35mm 4 core swa.
Armoured cable 10mm requires a smaller conductor than 16mm armoured cable as the armoured layer takes up more space, whereas the 6mm swa cable can have a smaller conductor.
● Insulation
The conductor’s insulation is usually a polymer such as PVC or XLPE. The application and the operating temperature will usually dictate the type of insulation used.
For example, armored wire for shed use will not need to withstand the same temperatures as armoured power cables used in industrial applications. The excellent dielectric strength of XLPE makes it the preferred choice for many high voltage applications.
● Bedding
The bedding layer is a polymer such as PVC, which helps to protect the inner components of armour cable from abrasion and mechanical damage. It is a protective layer between the insulation and the armour.
● Armour
The armour of armour cable is the component that makes it suitable for more hazardous applications. The armour layer can be steel wire armouring (SWA) or steel tape armouring (STA). STA is a thinner steel tape that is wrapped around the bedding layer. To withstand mechanical stresses, armouring is sometimes applied in multiple layers.
● Outer Sheath
The final layer is the outer sheath which can be PVC, LSZH, or PE. The application will usually dictate the type of sheath used. For example, an outdoor armoured cable will need an outer sheath resistant to UV light and weathering.
● Voltage
Each type of armour cable is manufactured with a specific voltage rating. The most common voltage ratings are 600/1000V, 6.35/11kV, and 19/33kV. With the increase in voltage, the thickness of the insulation and outer sheath is increased to maintain a dielectric strength that is adequate for the application.
Why Use Armoured Cables?
Armoured cables are commonly used in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications where a high degree of mechanical protection is required. The armour layer surrounding the conductor(s) can provide resistance to crushing, abrasion, impact damage, and penetration by sharp objects.
This makes armored wire an ideal choice for installations where there is a risk of the cable being subject to mechanical damage. To use an armour cable, you must ensure that you have the correct type of gland for the application.
When discussing applications of armour cable, the most crucial factor is the environment in which the cable will be used. Many factors can affect the suitability of armour cables, such as;
- The type of equipment that will be running on the cable
- The temperature of the surrounding environment
- The length of time that the cable will be in use
- The presence of any corrosive substances
Classification of Armored Cable
Armored cable has become tremendously popular in recent years. To classify them, there are three major types of armored cable. Each one is designed for different purposes. For example, some are used for computer networking, while others are designed specifically for home wiring. These include:
Type 1: SWA or Steel Wire Armour Cable
This is the most common type of armour cable. It gets its name from the steel wire surrounding the cable’s inner core. The main advantage of this type is that it is very strong and durable. This makes it ideal for use in high-traffic areas or locations where the cable is likely to be damaged.
Usually, this type of cable is used for high drop areas or for running cable through walls. When used in these applications, the steel wire helps to protect the inner core from damage. Cable SWA is most widely used in domestic and commercial applications.
Type 2: STA or Steel Tape Armour Cable
This type of armored wire is very similar to the SWA cable. The main difference is that instead of a steel wire, it has steel tape surrounding the inner core. The advantage of this type is that it is even more durable than SWA cable. This makes it ideal for buried-laying applications.
The main advantage of STA cable is that it is more resistant to damage from rodents. This is because the steel tape does not give them anything to grip on, making it much harder for them to gnaw through the jacket.
Type 3: AWA or Aluminium Wire Armored Cable
The third type of armour cable is AWA or aluminium armoured cable. This type gets its name from the inner core’s aluminum wire. The advantage of this type is that it is more flexible than either SWA or STA cable. Flexible armoured cable is often used in applications where the cable must be routed through tight spaces. Another advantage of this type is that it is lighter than either SWA or STA cable. This can make it easier to work with and install.
No matter the application, however, all three types of armoured cable have advantages and disadvantages. Before making a purchase, it is suggested that the customer evaluate their needs and then select the type of armored wire that is best suited for the job.
Armoured Cable vs. Unarmoured Cable: What’s The Difference?
As we know, power cables, and control cables are important for signal transmission or power supply in our daily life. There are mainly two types of cables; armored cable and unarmoured cable. But most people don’t know what the differences between them are. To help you have a better understanding of armour cable and unarmoured cable, the following points may be helpful.
Armour cable is a type of electrical cable reinforced with metal sheathing. The metal sheathing can be steel, aluminum, or other metals. Armored cable is used in applications where the cable needs to be buried in the ground or run through walls.
The metal sheathing protects the cable from being damaged by animals. The high-strength metal sheathing makes the armour cable resistant to fire and heat. Armouredcable price list varies as it is available in different sizes and specifications.
Compared to armored cable, the unarmoured cable does not have a metal sheathing. Unarmoured cable is typically used in control system applications and is unsuitable for burial or running through walls. Unarmoured cable is flexible than xlpe armoured cable and can be bent around corners. The lack of metal sheathing makes unarmoured cable lighter in weight than armored wire.
Unarmoured cables are more resistant to electromagnetic interference (EMI) than armour cables. The structure of an unarmoured cable is typically a core of one or more insulated conductors surrounded by a jacket. The most common type of unarmoured cable is UTP (unshielded twisted pair) cable. Usually, the unarmoured cable price is lower than armored cable as it is less complex to manufacture.
Nowadays, local municipalities and utility companies are requiring the use of armoured cables in new construction projects. The main reason is that armour cable is more resistant to damage than unarmour cable. Armoured cables enable faster installation time and can be run through walls without needing a conduit. In HT & LT distribution system, armour cables are used for underground duct and direct buried installation.
Please contact us if you need assistance choosing the right cable type for your application. The professional team of experts at ZW cable will be more than happy to help you select the right cable for your project.